Herniated disc and back pain? Seek immediate treatment to avoid surgery.
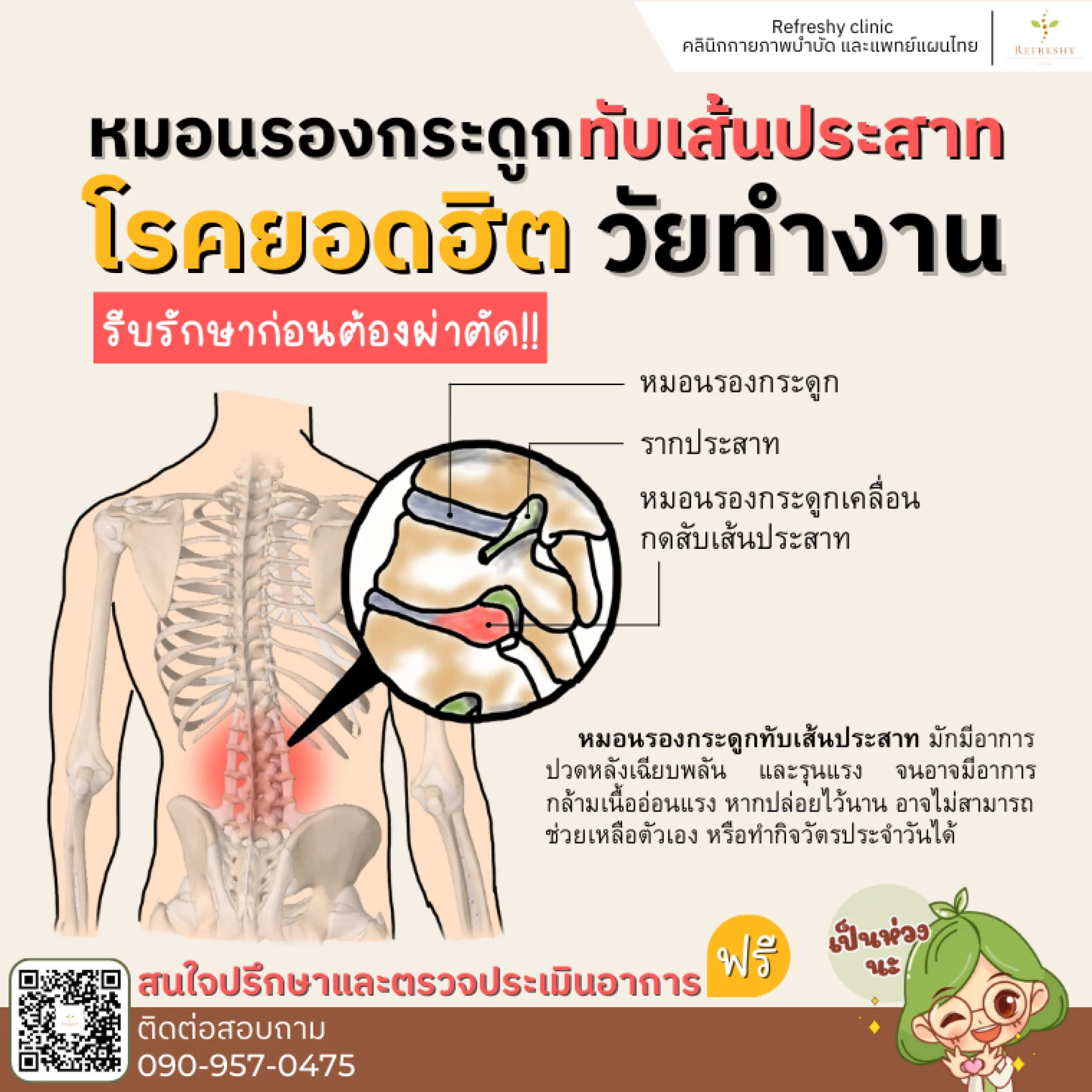
Herniated Disc: A Common Affliction in Mid-life!!
Seek treatment before surgery becomes necessary. Herniated disc disease often presents with chronic back pain, radiating numbness, and can escalate to muscle weakness. If left untreated, it may hinder self-sufficiency and daily activities.
Check for Herniated Disc Symptoms:
️⚠️ Lower Back Pain: Persistent pain or radiating pain down the leg.
️⚠️ Leg or Foot Numbness: Numbness or tingling sensations in the leg or foot.
️⚠️ Leg Weakness: Difficulty walking or standing due to leg weakness.
️⚠️ Radiating Leg Pain: Pain radiating from the back down to the buttocks, leg, or foot.
️⚠️ Muscle Spasms: Abnormal muscle tightness in the back and legs.
Q: Why does a herniated disc affect walking?
A herniated disc compressing a nerve disrupts nerve signals from the brain to leg muscles. Since the spinal cord connects the brain to body muscles, disc compression impairs communication between the brain and leg or foot muscles, leading to:
- Leg muscle weakness, causing difficulty walking and shorter strides.
- Impaired movement control and balance.
- Numbness or pain preventing normal walking.
Difficulty walking and poor balance from a herniated disc are not solely due to pain, but a complex effect of dysfunctional nervous and muscular systems. Untreated, it can lead to severe complications such as:
- Muscle Atrophy: Leg muscle shrinkage from disuse.
- Partial Paralysis: Nerve damage causing leg dysfunction.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Difficulty performing daily tasks.
Herniated Disc Severity Levels:
1. Early Stage: Disc degeneration causes chronic, intermittent back pain, gradually worsening.
2. Moderate Stage: Disc displacement or protrusion compresses nerves, causing radiating pain and numbness.
3. Severe Stage: Increased nerve compression leads to intensified pain, numbness, and weakness, risking nerve damage and disability.
This results from spinal overuse and degeneration, frequent bending, heavy lifting, prolonged driving, or extended sitting.
Therefore, frequent back pain warrants early examination and treatment to determine the best approach. Treatment is often simple and doesn't always require surgery.